The digestive system is the group of organs which are involved in the process of digestion. The digestion is the process of transforming food so that it can be absorbed and used by the body's cells.
Parts:
Mouth: The mouth is composed of: the teeths, the tongue and the salivary glands.
Pharynx: The pharynx, is a funnel-shaped tube connected to the posterior end of the mouth. The pharynx is responsible fot the passing of masses of chewed food from the mouth to the esophagus. The pharynx serves two different functions, it contains a flap of tissue known as the epiglottis that acts as a switch to route food to the esophagus and air to the larynx.
Esophagus: The esophagus is a muscular tube connecting the pharynx to the stomach that is part of the upper gastrointestinal tract. It carries swallowed masses of chewed food along its lenght. At the inferior end of the esophagus is a muscular ring called the lower stomach. gallbladder and pancreasesophageal sphincter or cardiac sphincter. The function of this sphincter is to close of the end of the esophagus and trap food in the stomach.

Stomach: The stomach is a muscular sac that is located on he left side of the abdominal cavity. In a person, the stomach is about size of their two fists. This major organ acts as a storage tank for food so that the body has time to digest large meals properly.
Small intestine: The small intestine is located just inferior to the stomach and takes up most of the space in the abdominal cavity. The entire small intestine is coiled. By the time food leaves the small intestine . all nutrients have been extracted.
Liver and gallbladder: The liver is a organ of the digestive system located to the right of the stomach. The liver is the second largest organ in the body.
The gallbladder is a small organ located just posterior to the liver. The gallbladder is uses to store and recycle fot the digestion of subsequen meals.
Pancreas: The pancreas is a large gland located just inferior and posterior to the stomach. The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine to complete the chemical digestion of foods.
Large intestine: The large intestine is a long, thick tube It is located just inferior to the stomach and wraps around the superior border of the small intestine. The large intestine contains many simbiotic bacteria. Feces in the large intestine exit the body through the anal canal.
Relationship between systems: Digestive system breaks down large molecules into simple molecules such as glucose. These are then transported to cells of the body via the circulatory system.
The respiratory system causes the diffusion of oxygen into the blood and the diffusion of CO2 out of the blood. This oxygen is then transported to cells of the body via the circulatory system.
When the cells have both oxygen and glucose they can respire to release energy, producing water and carbon dioxide (the CO2 is carried through the circulatory system to the lungs where it is removed through the respiratory system.
THE END
THANKS FOR READING IT.

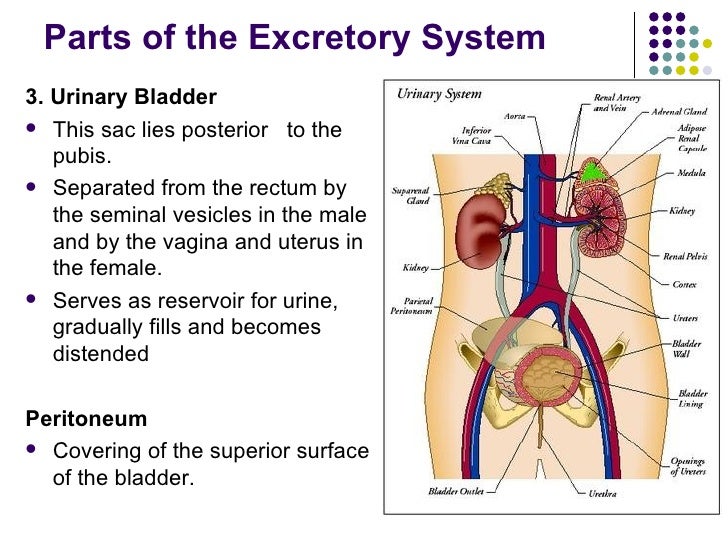


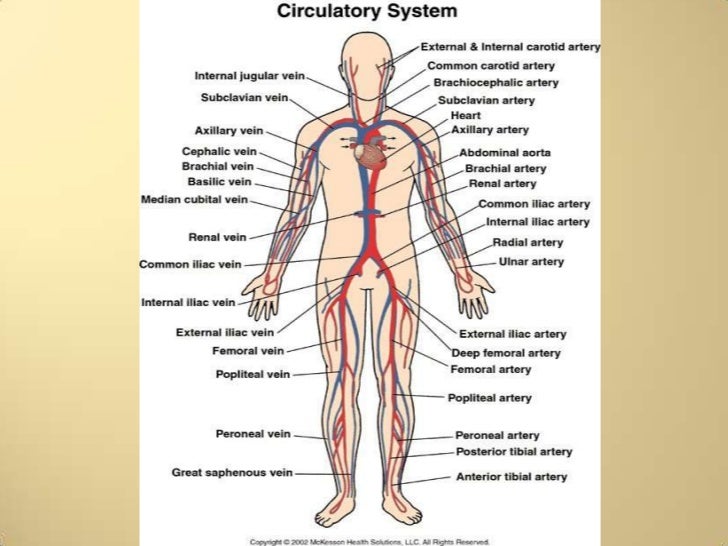
/vasos-sanguineos-sistema-cardiovascular-56a299c13df78cf77277f46b.jpg)
